Trichology
"From Hair Woes to Hair Wow: Unveiling the Latest Breakthroughs in Hair Treatment and Hair Loss"

Hair Loss Treatment:
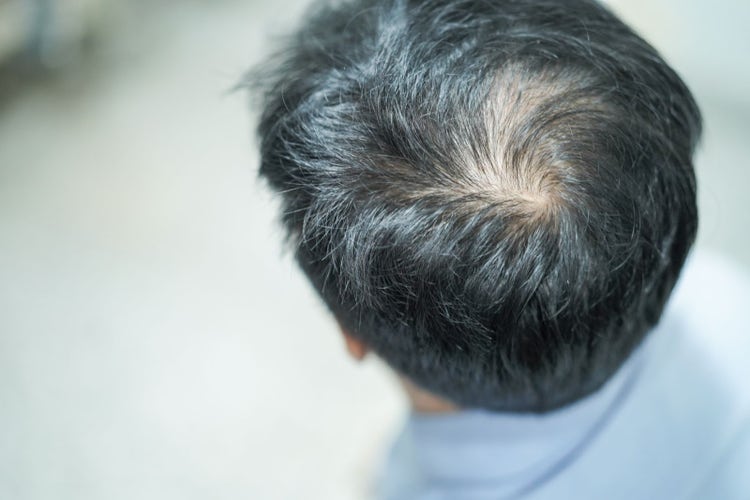
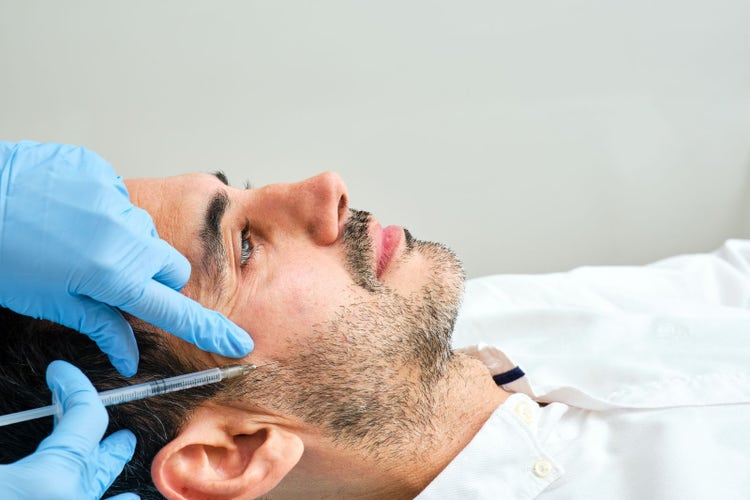
PRP scalp therapy is commonly used to treat hair loss, specifically androgenetic alopecia (pattern baldness) in both men and women. The growth factors and proteins present in platelets stimulate dormant hair follicles, promote hair regrowth, and increase hair thickness and density.
Hair Thinning:
PRP scalp therapy can help address hair thinning or fine hair by strengthening existing hair follicles and encouraging the growth of thicker, healthier hair strands.
Scalp Health Improvement:
PRP therapy can improve the overall health of the scalp by increasing blood circulation, promoting the regeneration of cells, and reducing inflammation. It can help alleviate scalp conditions like dandruff, dryness, and itchiness.
Post-Hair Transplant Support:
PRP scalp therapy is often used as a complementary treatment after hair transplantation procedures. It can help accelerate the healing process, enhance graft survival, and promote hair growth in transplanted areas.


Hair Maintenance and Prevention:
PRP therapy can be used as a proactive approach to maintain hair health and prevent future hair loss. Regular PRP scalp treatments can help slow down the progression of hair loss and preserve existing hair follicles.

Hair Loss Treatment:
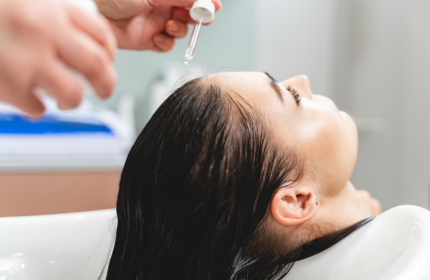
Mesotherapy scalp treatment is commonly used to address hair loss and promote hair regrowth. The injected cocktail of nutrients and growth factors nourishes the hair follicles, stimulates blood circulation, and promotes the growth of new, healthy hair.
Hair Thickening and Strengthening:
Mesotherapy can help improve the thickness and strength of the existing hair strands. The nutrients delivered directly to the scalp nourish the hair follicles, which can result in thicker and stronger hair growth.


Scalp Health Improvement:
Mesotherapy can improve the overall health of the scalp by providing essential nutrients and promoting better blood circulation. It can help alleviate scalp conditions like dryness, itchiness, and inflammation.
Hair Quality Enhancement:
Mesotherapy can enhance the overall quality of the hair by improving its texture, shine, and manageability. The nutrients injected during the treatment can support healthier hair growth and contribute to a more vibrant appearance.
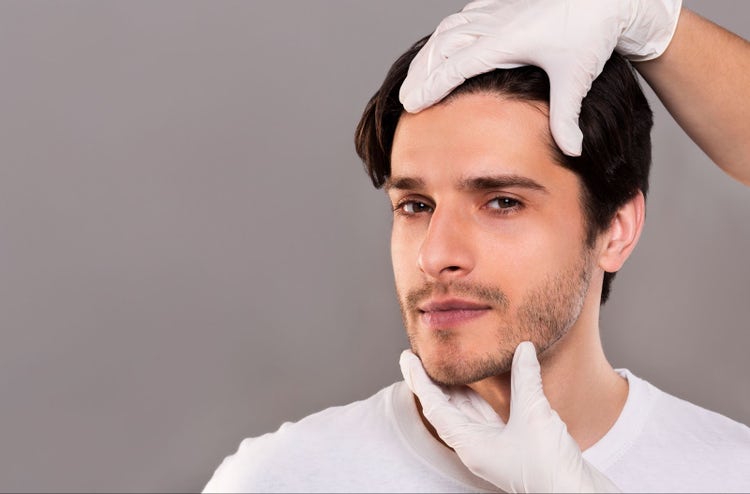
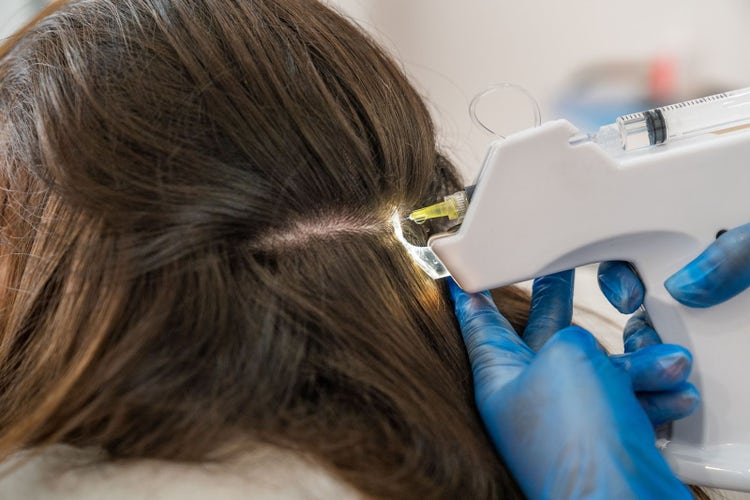

Post-Hair Transplant Support:
Mesotherapy is often used as a complementary treatment after hair transplantation procedures. It can promote healing, enhance graft survival, and improve the overall success of the transplantation by providing essential nutrients to the newly transplanted hair follicles.
Growth Factor PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma) refers to a specialized form of PRP therapy that is enriched with additional growth factors. Here are some of the primary uses
and benefits of Growth Factor PRP:
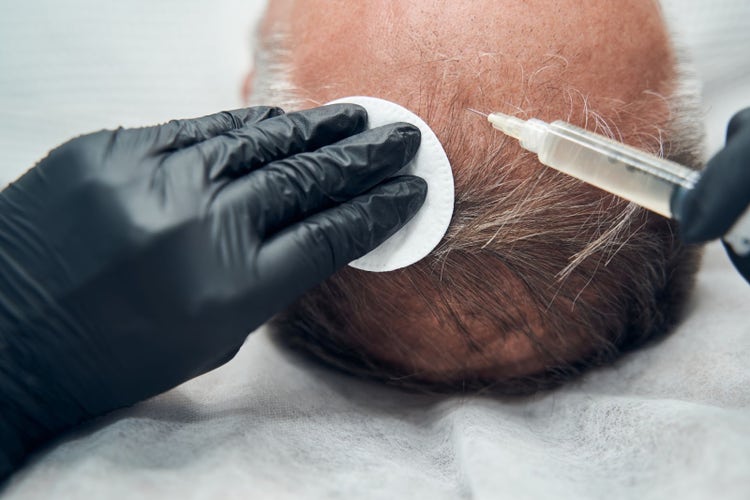
Hair Loss Treatment:
Growth Factor PRP therapy is commonly used to treat hair loss, particularly androgenetic alopecia (pattern baldness). The growth factors present in PRP stimulate hair follicles, promote hair regrowth, and increase hair thickness and density. The addition of extra growth factors in Growth Factor PRP can enhance the effectiveness of the treatment.
Hair Restoration:
Growth Factor PRP can be utilized for hair restoration procedures, such as hair transplant surgeries. When used in combination with hair transplantation, Growth Factor PRP can improve graft survival rates, promote healing, and accelerate the recovery process.
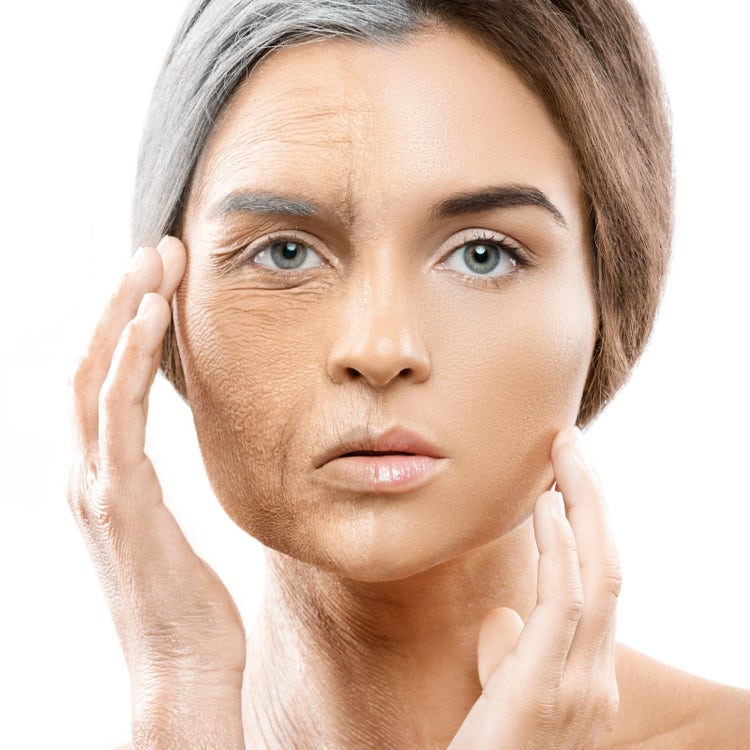
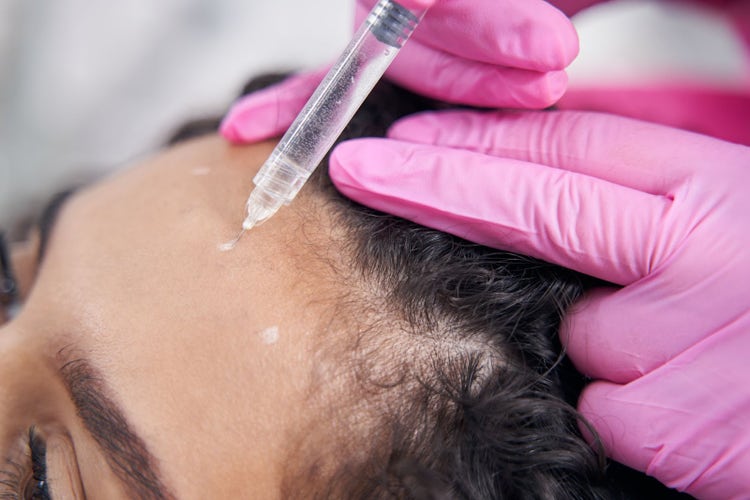

Anti-Aging and Skin Rejuvenation:
Growth Factor PRP can be used for facial rejuvenation treatments. The growth factors and other bioactive substances in PRP promote collagen production, improve skin elasticity, and enhance overall skin texture and tone.
Wound Healing:
Growth Factor PRP has applications in wound healing and tissue regeneration. The growth factors in PRP help stimulate the body's natural healing process, accelerate tissue repair, and improve the overall healing outcomes for wounds, ulcers, or surgical incisions.

Anti-Dandruff Shampoos:
The primary treatment for dandruff involves using anti-dandruff shampoos. These shampoos typically contain active ingredients that help reduce the production of skin cells, control scalp inflammation, and combat the underlying causes of dandruff. The most common active ingredients found in anti-dandruff shampoos include:
•Zinc pyrithione:
Effective against dandruff-causing fungus and helps control flaking.
•Selenium sulfide: Reduces the production of skin cells and controls malassezia fungus.
• Ketoconazole: An antifungal agent that helps eliminate the fungus associated with dandruff.
• Coal tar: Slows down the rate of skin cell turnover and reduces inflammation.
• Salicylic acid: Exfoliates the scalp and helps remove dead skin cells.
Regular Shampooing:
Washing your hair regularly helps remove excess oil, dead skin cells, and dandruff flakes from the scalp. Use a gentle shampoo that is suitable for your hair type and follow with a conditioner to keep your hair moisturized.


Avoiding Triggers: Certain factors can exacerbate dandruff symptoms.
Avoiding or minimizing these triggers can help manage dandruff. Common triggers include:
•Dry scalp: Keep your scalp moisturized by using a conditioner or applying a moisturizer specifically formulated for the scalp.
•Irritants: Avoid using hair care products that contain harsh chemicals or irritants that can further inflame the scalp.
•Stress: Manage stress levels through relaxation techniques, exercise, and sufficient sleep, as stress can worsen dandruff symptoms.
• Diet: A balanced and healthy diet rich in vitamins and minerals may contribute to a healthier scalp.

Medications:
•Minoxidil: Available as a topical solution or foam, minoxidil is the only FDA-approved over-the-counter medication for hair loss treatment. It is applied directly to the scalp and can promote hair regrowth in both men and women.
•Finasteride: This prescription medication is primarily used for male pattern baldness. It works by inhibiting the conversion of testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone that contributes to hair loss. Finasteride can help slow down hair loss and promote hair regrowth in some individuals.
Hair Transplantation:
•Hair transplantation is a surgical procedure that involves harvesting hair follicles from a donor area and implanting them into the balding or thinning areas of the scalp. It is a suitable option for individuals with permanent hair loss and can provide natural-looking, long-term results.
Laser Therapy:
•Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT) devices emit red light wavelengths that stimulate hair follicles, increase blood circulation, and promote hair growth. These devices can be used at home or administered in clinics as part of a treatment plan.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy:
• PRP therapy involves extracting a patient's blood, processing it to concentrate platelets, and injecting the platelet-rich plasma into the scalp. The growth factors present in platelets can stimulate hair follicles and promote hair regrowth.
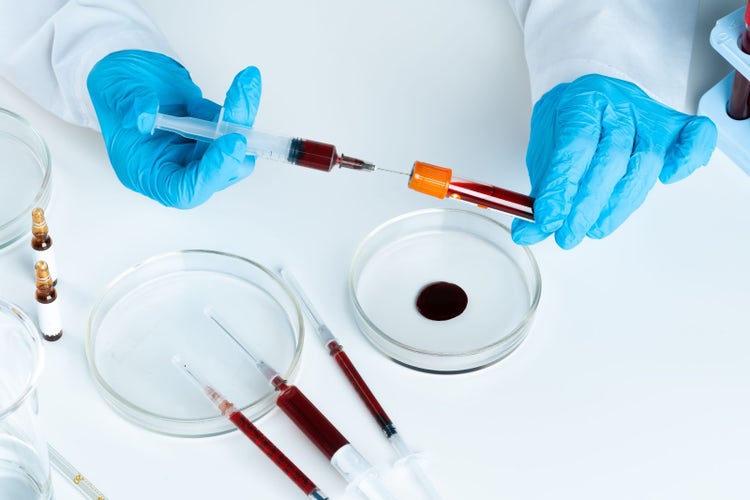

Prescription Medications:
•In cases of hair loss caused by specific conditions, such as alopecia areata, autoimmune-related hair loss, or hormonal imbalances, prescription medications may be recommended. These medications are prescribed by a healthcare professional based on the underlying cause and may include corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, or hormone therapy.
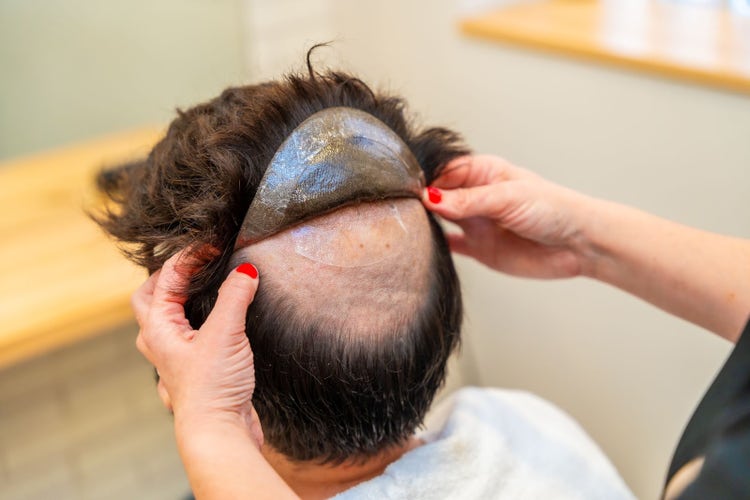
Scalp Micropigmentation (SMP):
• SMP is a non-surgical cosmetic procedure that involves tattooing tiny pigments onto the scalp to replicate the appearance of hair follicles. It can be used to create the illusion of a full head of hair, camouflage bald patches, or create the look of a closely shaved head.
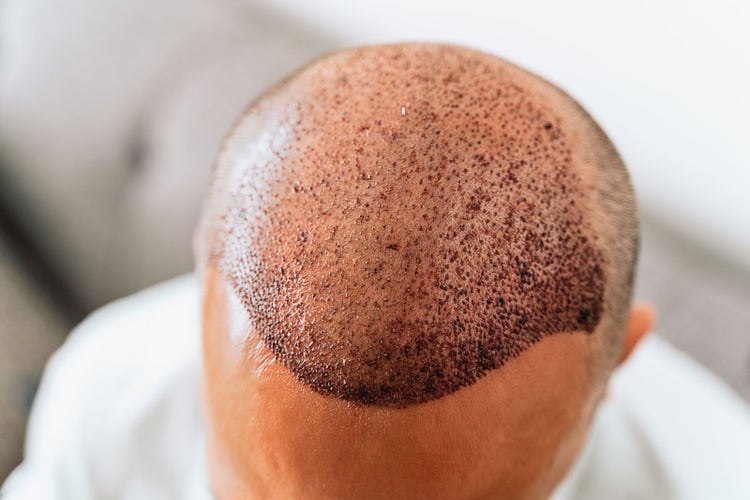
1. Medications:
•Minoxidil: Minoxidil is an over-the-counter topical solution or foam that is directly applied to the scalp. It is available in different strengths and is commonly used to treat androgenetic alopecia (pattern baldness) in both men and women. Minoxidil is thought to prolong the growth phase of the hair follicles, leading to increased hair density and thickness.
Finasteride: Finasteride is an oral prescription medication primarily used for male pattern baldness. It works by blocking the conversion of testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone that contributes to hair loss. Finasteride can help slow down hair loss and promote hair regrowth in some individuals, but it is generally not recommended for women of childbearing age due to potential risks to a developing fetus.
2 . Laser Therapy:
• Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT): LLLT uses red light wavelengths to stimulate hair growth. It is typically administered through laser combs, caps, or helmets. The lasers penetrate the scalp and stimulate blood circulation, enhance cell metabolism, and promote hair regrowth. LLLT is often used as an adjunctive treatment with other regrowth methods.
3. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy:
• PRP therapy involves drawing a patient's blood, processing it to concentrate the platelets, and injecting the platelet-rich plasma into the scalp. Platelets contain growth factors that can potentially stimulate hair growth and improve the health of hair follicles. PRP therapy is commonly used for androgenetic alopecia and can be performed in combination with other treatments.
4. Hair Transplantation:
• As mentioned in the previous response, hair transplantation is a surgical procedure that involves transplanting hair follicles from a donor area to the balding or thinning areas of the scalp. It is an effective way to restore hair in areas of permanent hair loss, providing a long-term solution.
5. Nutritional Supplements:
• Certain nutritional supplements, such as biotin, vitamins (e.g., vitamin D, vitamin E), and minerals (e.g., zinc, iron), are believed to support healthy hair growth. However, it's important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any supplements to determine if they are appropriate for your specific needs.
1. Procedure of Hair transplantation : It is typically performed under local anesthesia on an outpatient basis. The two most commonly used techniques are:
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT): In this method, a strip of scalp containing hair follicles is surgically removed from the donor area, and the wound is sutured. The strip is then divided into individual grafts containing one to four hair follicles, which are implanted into the recipient area.
• Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE): FUE involves the extraction of individual hair follicles directly from the donor area using a punch-like instrument. These follicles are then implanted into the recipient area.